RD Sharma Solutions For Class 7 Chapter 19 – Visualising Solid Shapes
Exercise 19.1 Page No: 19.3
1. Complete the following table and verify Euler’s formula in each case.

Solution:
(i) We know that Euler’s formula is (F – E + V)
(F – E + V) = (6 – 12 + 8) = 2
Hence Euler’s formula verified
(ii) We know that Euler’s formula is (F – E + V)
(F – E + V) = (4 – E + 4) = 2.
E = 6
Hence Euler’s formula verified
(iii) We know that Euler’s formula is (F – E + V)
From the figure,
(F – E + V) = (9 – 16 + 9) = 2.
Hence Euler’s formula verified
(iv) We know that Euler’s formula is (F – E + V)
From the figure,
(F – E + V) = (7 – 15 + 10) = 2.
Hence Euler’s formula verified
2. Give three examples from our daily life which are in the form of
(i) A cone
(ii) A sphere
(iii) A cuboid
(iv) A cylinder
(v) A pyramid.
Solution:
(i) Examples for Cone: Ice-cream cone, birthday cap
(ii) Examples of Sphere: Football, a round apple, an orange
(iii) Examples of Cuboid: dice, duster, book, rectangular box
(iv) Examples of Cylinder: circular pipe, glass, circular pole, gas cylinder
(v) Examples for Pyramid: Christmas tree, prism
Exercise 19.2 Page No: 19.5
1. Match the following nets with appropriate solids:
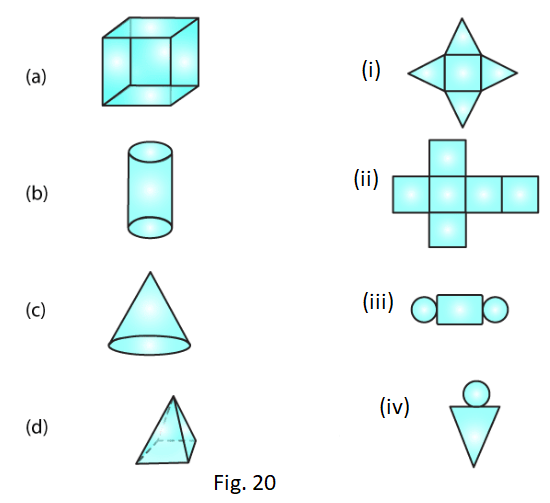
Solution:
(a) → (ii)
(b) → (iii)
(c) → (iv)
(d) → (i)
2. Identify the nets which can be used to make cubes (cut-out the nets and try it):
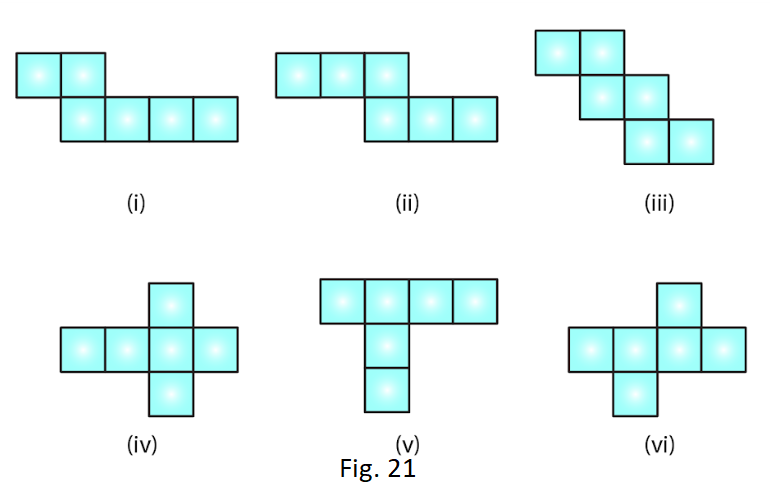
Solution:
Only (ii), (iv) and (vi) form a cube.
3. Can the following be a net for a die? Explain your answer.
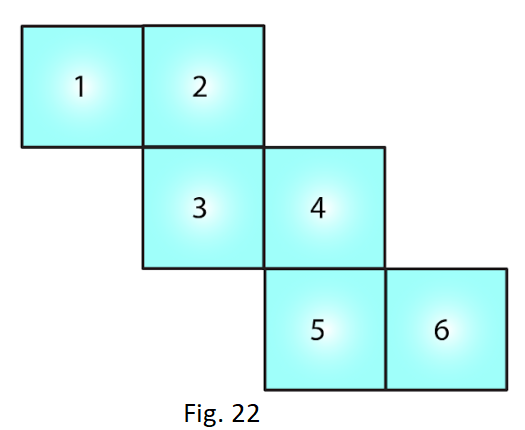
Solution:
We know that in a die, the sum of the number of opposite faces of a die is 7. In the given figure, it is not possible to get the sum as 7. Hence the given net is not suitable for a die.
4. Out of the following four nets there are two correct nets to make a tetrahedron. Identify them.
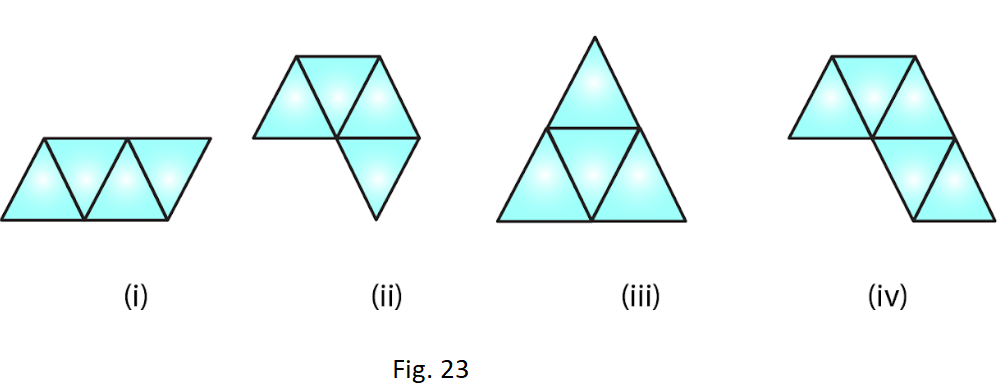
Solution:
For making a tetrahedron, only (i) and (iii) are suitable nets.
5. Here is an incomplete net for making a cube. Complete it in at least two different ways.
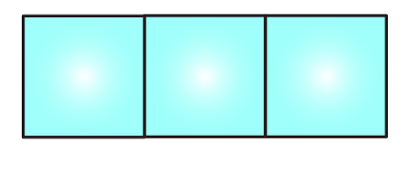
Solution:
Comments
Post a Comment